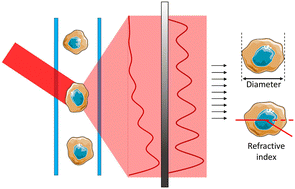
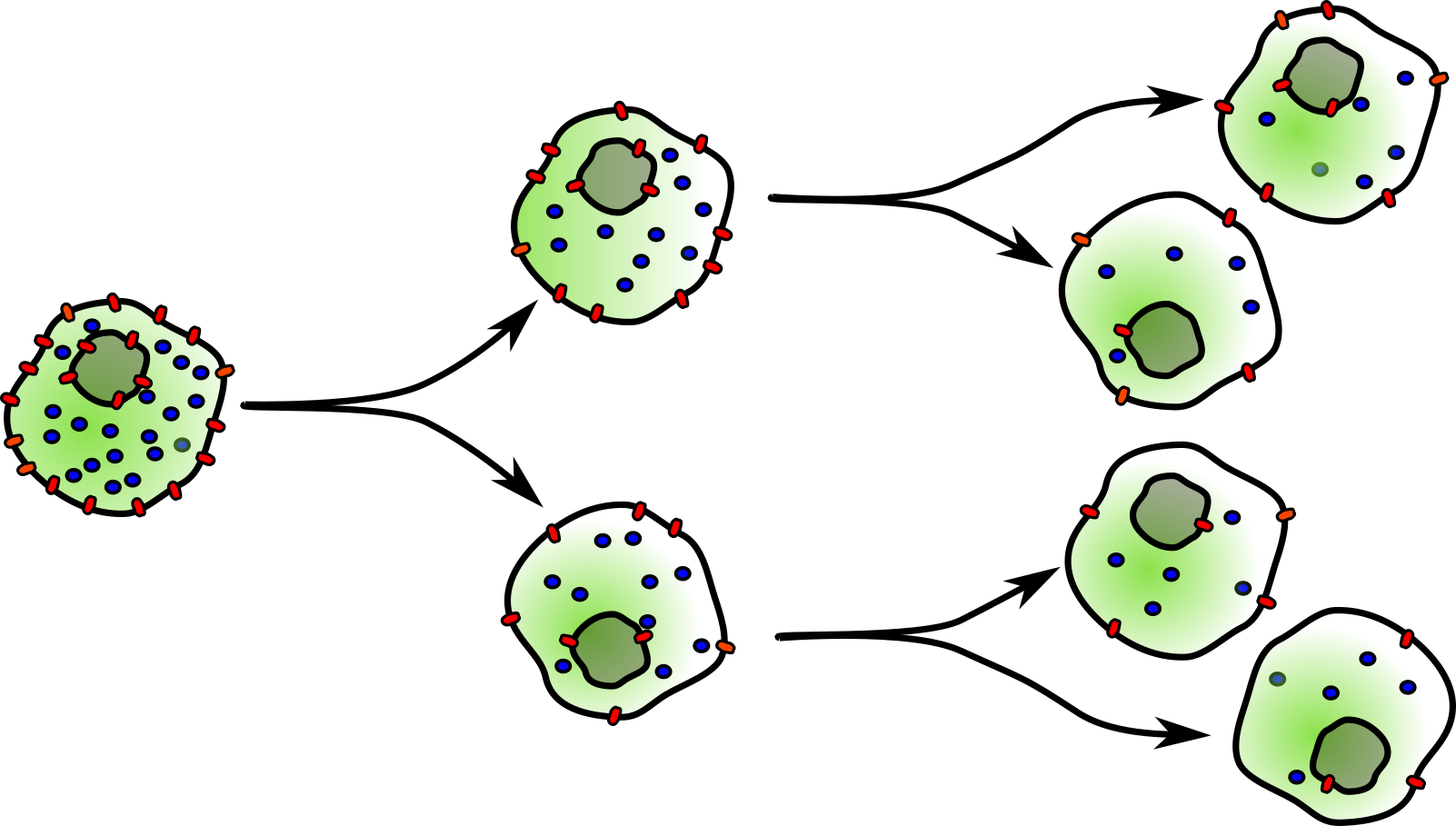
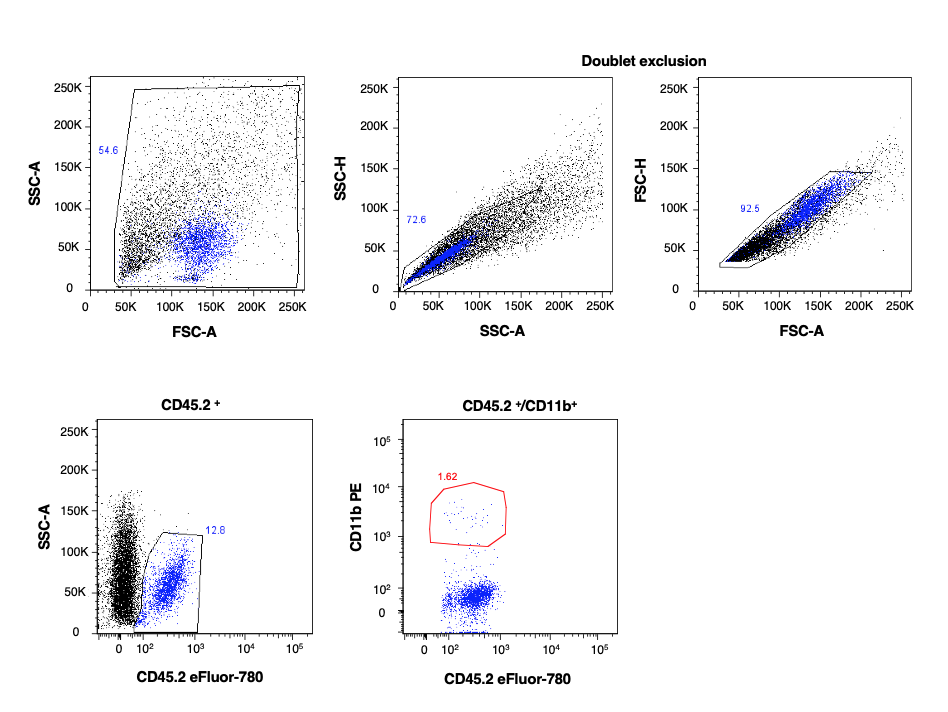
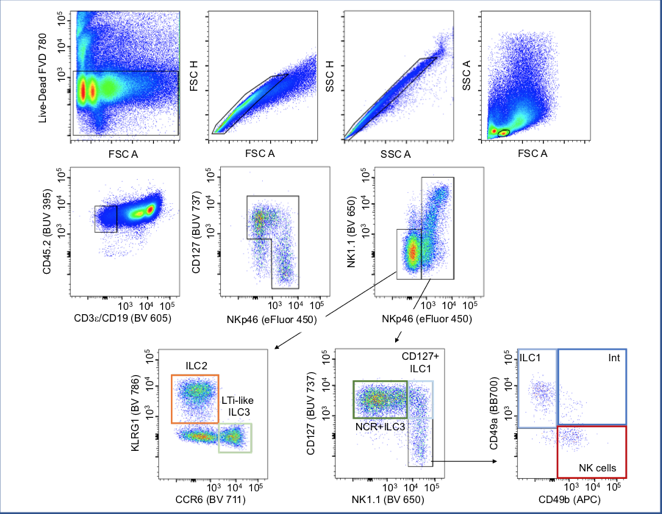
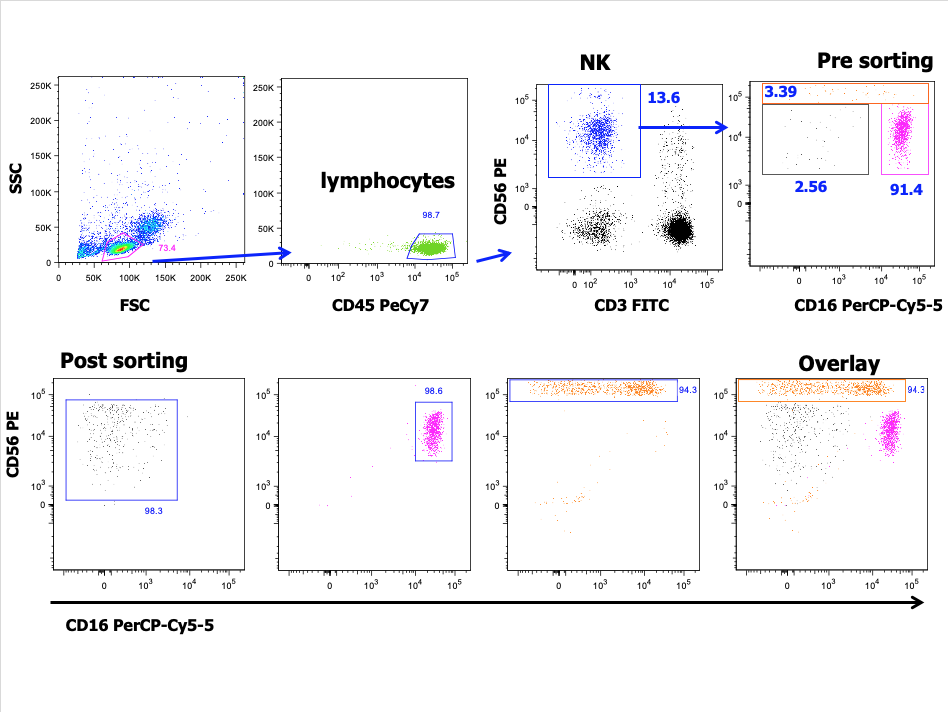
The technology of these machinery allows simultaneous multiparametric analysis of thousands of cells for second for rapid analysis of complex cell populations. This is achieved by the use of different labeled antibodies or dyes to target specific molecules express at the surface or in the cytoplasm of the cell, giving a screening able to describe in detail a complex sample or to identify low frequency subset of cells.
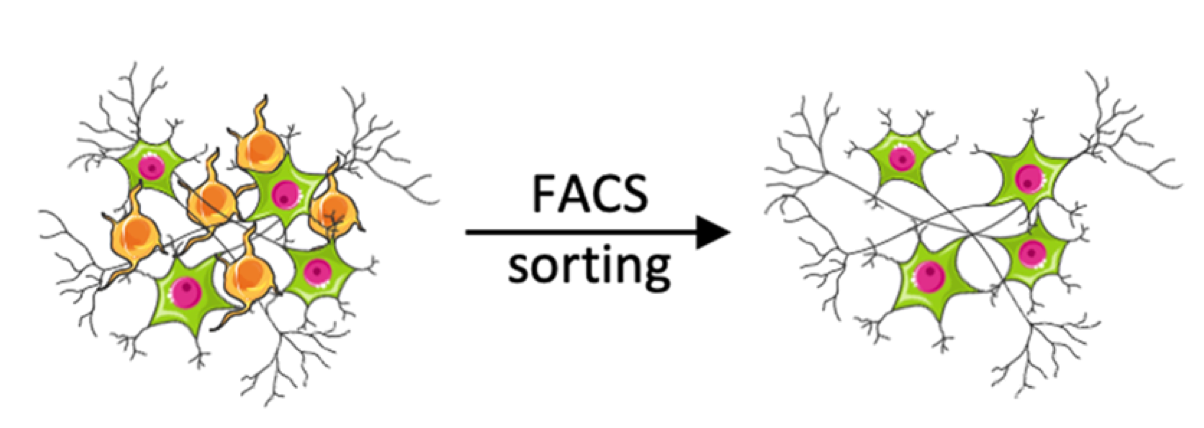
Through these instruments, a variety of fluorochromes attached to different antibodies can screen the molecular components of a cell first to characterize it (flow cytometer) and then to specifically select it for isolation (cell sorter).
The Flow Cytometry laboratory offers experimental setup/panel design, samples acquisition, sample isolations, data analysis when required and data management. The laboratory support IIT projects and collaborative research projects with Sapienza community and other institutions.